Multitenant environments
IBM® Cognos® Business Intelligence provides built-in multitenancy capabilities. Existing deployments of Cognos Business Intelligence can be incrementally migrated to implement multitenant capabilities. The existing deployments that do not use multitenant capabilities are not affected if multitenancy is enabled.
All Content Manager objects can have a single, optional tenant ID. All Cognos users, including administrators, can have an optional tenant ID. Cognos users cannot, regardless of the Cognos BI security policies, access a Content Manager object if they do not have a tenant ID that matches the Content Manager object tenant ID. Content Manager objects that do not have a tenant ID are considered public and can be accessed by any user. Users who do not have a tenant ID can access only public objects.
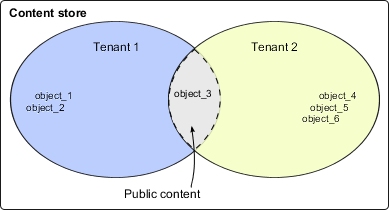
- Users that belong to Tenant 1 can access object_1, object_2, and object_3.
- Users that belong to Tenant 2 can access object_3, object_4, object_5, and object_6.
When accessing objects, object tenancy is evaluated before object access permissions. Therefore, users in a multitenant application see only the objects that are associated with their tenant and objects that are categorized as public.
After multitenancy is enabled, you can record tenant activities using an audit logging database. IBM Cognos BI provides sample audit reports that show how to use the tenancy information to monitor certain user activities. For information about how to use IBM Cognos Configuration to set up a logging database, see the IBM Cognos Business Intelligence Installation and Configuration Guide. For information about setting up the sample audit reports, see Sample Audit Model and Audit Reports.
